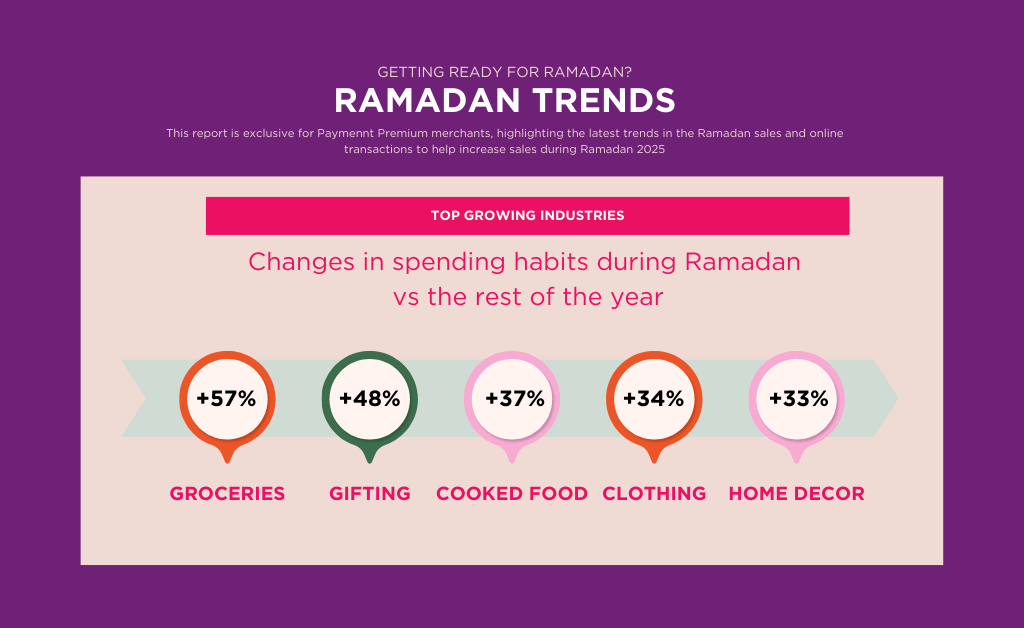
Leveraging marketplaces like Amazon, Talabat, and Zbooni for online payments offers merchants several advantages, including access to a vast customer base, robust payment infrastructure, and advanced fraud protection. This can significantly simplify the process of setting up a merchant’s own website and payment system, as marketplaces assume some financial risks and product setup responsibilities.
Marketplaces typically provide a diverse range of payment options, such as credit and debit cards, e-wallets, and bank transfers, enhancing the likelihood of successful transactions. Additionally, they offer essential merchant services like shipping and handling, customer support, and returns, saving merchants valuable time and resources.
While these platforms provide convenience, they are not intended to be used as sole payment providers. These platforms offer a comprehensive ecosystem for selling products, but merchants should be mindful of the potential risks associated with relying solely on them for payments
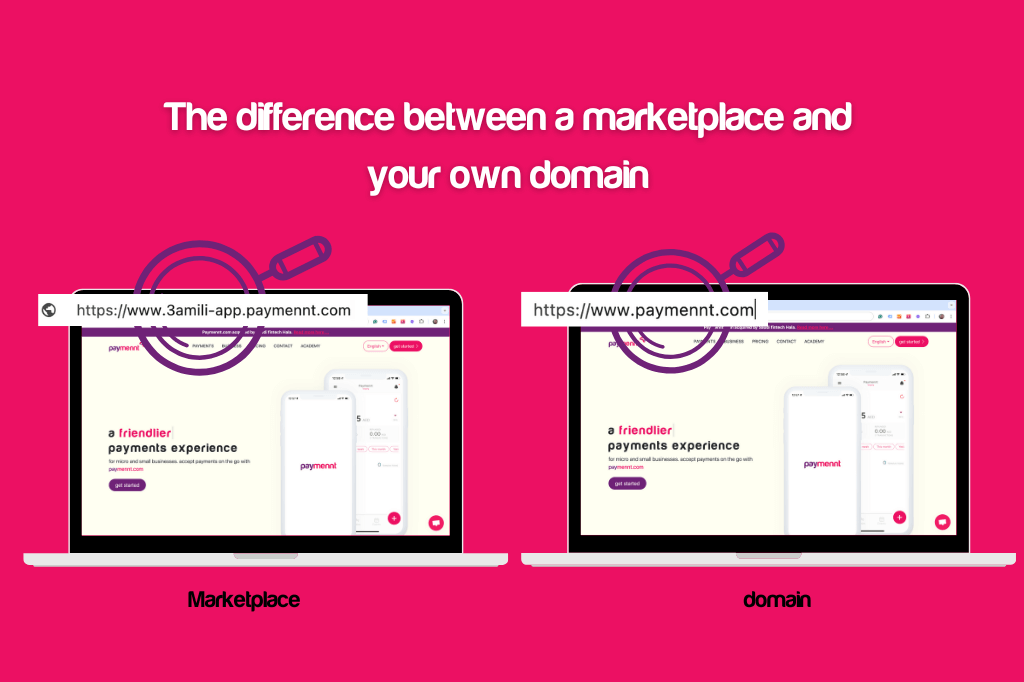
Below are some of their shortcomings and things to watch out for when processing payments on marketplaces:
Chargebacks on Marketplaces
Many marketplaces rely on third-party payment gateways, which means the marketplace is listed on the customer’s card statement rather than the merchant. This introduces an additional layer between the merchant and the customer, potentially complicating dispute resolution. If a dispute arises, merchants using marketplaces may be subject to the marketplace’s dispute resolution process, which could result in unfavorable outcomes or additional fees.
In contrast, payment gateways typically offer direct dispute resolution centers, allowing merchants to work directly with the gateway to resolve issues and claims. This provides greater control and protection in the event of chargebacks
The Fee Structure in Marketplaces
Marketplaces generally charge higher payment processing fees compared to direct payment gateways. These fees can be substantial, especially for services like payment links and single-item sales where merchants have direct relationships with their customers.
Customer experience
Merchants using marketplaces often face limitations in customizing the customer experience. Marketplace policies and procedures, which may not align with the merchant’s business model, can restrict flexibility. This includes the design of the merchant’s page and strict refund and return policies that merchants may be forced to adopt
Marketplaces Security and regulation
While many marketplaces claim PCI compliance, it’s essential to verify their security measures. Some marketplaces may not be regulated and still accept payments, increasing the risk of data breaches and compromised customer information. Merchants must carefully evaluate marketplace security to protect their reputation and customer data.
Using a standalone payment gateway ensures PCI compliance, safeguarding both merchant and customer data. However, it also places the responsibility for customer support, dispute resolution, and fraud prevention solely on the merchant. Partnering with a reputable payment gateway can mitigate these risks, providing valuable protection against fraud and chargebacks, especially for small businesses.
By using a standalone payment gateway, merchants can avoid the additional costs and complexities associated with implementing their own security measures and fraud detection systems
Paymennt.com is a PCI-compliant payment gateway, with a dedicated dispute center to help merchants through any disputes and chargebacks. We also actively advise clients on how to prevent chargebacks and good online payment hygiene. Get in touch with paymennt.com today to learn more.